Manufacturing applications are pivotal in today’s industrial landscape. They encompass a range of technologies that enhance production efficiency and quality. According to recent industry reports, the manufacturing sector is projected to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.0% from 2023 to 2028. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on innovative applications in manufacturing processes.
These applications serve various purposes, such as automation, supply chain management, and quality control. For instance, a survey by the International Data Corporation (IDC) indicated that 75% of manufacturers use automation to reduce labor costs. However, the implementation of manufacturing applications is not without challenges. Companies must invest in training and infrastructure, yet many fail to foresee these complexities.
The benefits of adopting advanced manufacturing applications are clear. They can drastically improve efficiency and reduce waste. However, companies often overlook the ongoing need for adaptation and continuous improvement. As the landscape evolves, so must the applications that drive success in manufacturing. Exploring these tools is essential for future sustainability and competitiveness.

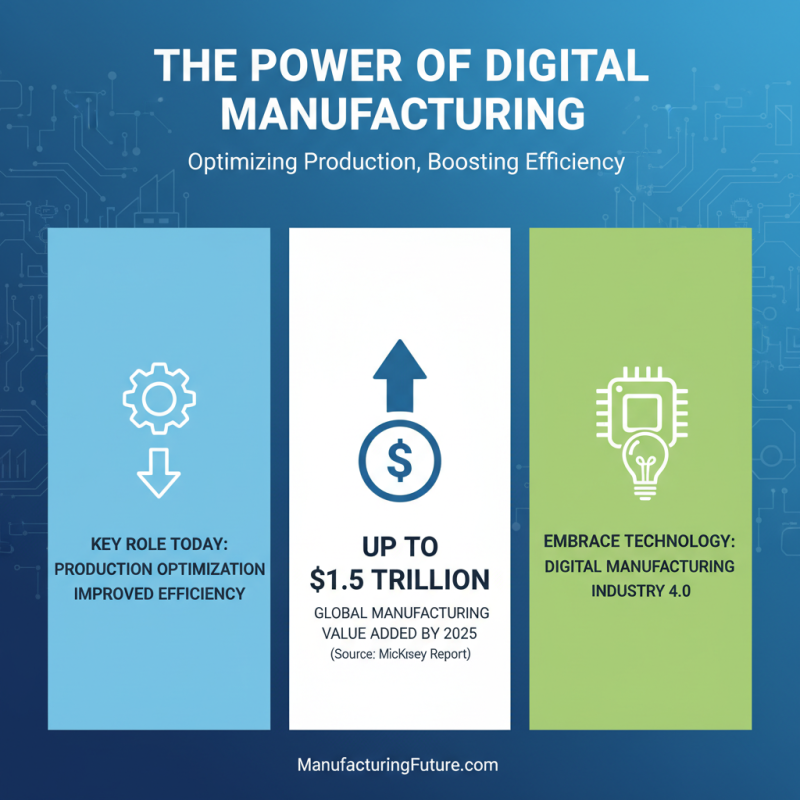
Manufacturing applications play a crucial role in the industry today. They enable companies to optimize production processes and improve efficiency. According to a report by McKinsey, digital manufacturing could add up to $1.5 trillion in value to global manufacturing by 2025. This figure highlights the significance of embracing technology in manufacturing.
Many manufacturers use these applications to streamline operations. For instance, predictive maintenance applications can reduce downtime by 30% or more. This reduces costs and increases productivity. However, not all manufacturers leverage these technologies effectively. A survey by Deloitte found that over 60% of manufacturers struggle with data management and integration across systems. These challenges can hinder the full potential of manufacturing applications.
Additionally, the proliferation of automation raises concerns about the workforce. As machines take on more tasks, the demand for skilled labor fluctuates. Some workers may find their roles obsolete. The World Economic Forum predicted that 85 million jobs could be displaced by automation by 2025. Balancing technology adoption with workforce needs is essential for sustainable growth.
Manufacturing applications play a crucial role in various industries. Key sectors utilizing these applications include automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods, and pharmaceuticals. Each industry faces unique challenges that manufacturing applications help address.
In automotive manufacturing, applications streamline assembly lines. They improve quality control and enhance production efficiency. Real-time data tracking minimizes errors. In aerospace, the focus is on precision. Manufacturing applications ensure parts meet strict regulations. This reduces risks associated with safety.
**Tip:** Regular training for employees can boost application effectiveness. Keeping them updated on new technologies matters.
Electronics manufacturing benefits from rapid prototyping. Speed is crucial in this competitive industry. Applications facilitate quicker design adjustments. Consumer goods require adaptability. Manufacturing applications allow for flexibility in production. Meeting consumer demand becomes easier.
**Tip:** Evaluate workflows periodically to spot inefficiencies. Small tweaks can lead to significant improvements.
Pharmaceuticals face stringent safety standards. Applications assist in adhering to compliance regulations. They ensure consistent production quality. Yet, embracing technology can be challenging. Some employees resist change. Addressing their concerns is vital for success.
Manufacturing applications play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency. They allow companies to streamline processes and reduce costs. These applications also facilitate better inventory management. When implemented effectively, they can lead to substantial time savings.
One significant benefit is improved production accuracy. By utilizing automation, errors decrease. This leads to better quality control. Companies can produce consistent products, which ensures customer satisfaction. Additionally, real-time data helps managers make informed decisions. However, setting up these systems can be complex. Training staff properly is essential.
Another advantage is enhanced collaboration. Manufacturing applications promote communication among teams. This coordination can improve project timelines. But, challenges remain in integrating new tools with existing systems. Users often experience a learning curve. Adapting takes time and patience, which can sometimes be frustrating.
Manufacturing applications face numerous challenges that can hinder efficiency. One common issue is equipment downtime. Machines often break down unexpectedly, leading to production delays. Regular maintenance can help, but it may not always suffice. Workers need training to handle minor issues quickly. However, skill gaps can exist, leaving teams unprepared.
Another significant challenge is supply chain disruptions. Unexpected events, like natural disasters or political changes, impact material availability. This leads to project delays and increased costs. Manufacturers must develop flexible supply chains. Building relationships with multiple suppliers can mitigate risks. Yet, coordination issues may arise, complicating these solutions.
Quality control is another concern. Maintaining high standards is essential, but inconsistencies often occur. Errors in production can lead to defective products. Implementing automated inspection systems can reduce mistakes. Still, reliance on technology raises questions about effectiveness. Continuous monitoring and adjustment are necessary to ensure reliability.
The manufacturing landscape is rapidly changing. Emerging technologies are shaping how industries operate. According to a report by McKinsey, 70% of manufacturers plan to invest in automation by 2025. This reflects a growing trend towards efficiency and precision in manufacturing applications.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are at the forefront of this evolution. For instance, predictive maintenance can reduce downtime by up to 30%. This not only saves costs but also enhances productivity. However, challenges remain. Many companies struggle to integrate these technologies effectively.
Data security is another pressing concern. As manufacturers collect more data, the risk of cyber threats increases. Studies show that 60% of manufacturers experienced a data breach in the last year. Companies need to be cautious and develop robust security protocols. These future trends highlight both the potential and the pitfalls in manufacturing applications technology.
| Application Area | Key Features | Benefits | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Management | Real-time tracking, Inventory optimization | Increased efficiency, Cost reduction | AI integration, Blockchain technology |
| Quality Control | Automated inspections, Data analytics | Reduced defects, Enhanced product quality | IoT sensors, Predictive maintenance |
| Production Planning | Scheduling algorithms, Resource allocation | Optimized workflows, Reduced lead times | Machine learning, Adaptive planning systems |
| Research and Development | Simulation tools, Prototyping | Faster time-to-market, Innovation acceleration | Digital twins, Augmented reality |
| Maintenance Management | Predictive analytics, Condition monitoring | Reduced downtime, Lower maintenance costs | AI-driven insights, Remote monitoring |




We’re here to help and answer your questions.